Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Mri | Ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine is associated with facet joint degeneration: We have already covered the most common site: An mri study found that ligamentum flavum thickness was over 3.0 mm thick, and in many it was over 3.5 mm thick 17. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies.
The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. Understanding your mri of the lumbar spine these pictures of this page are about:ligamentum. Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course: As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal.
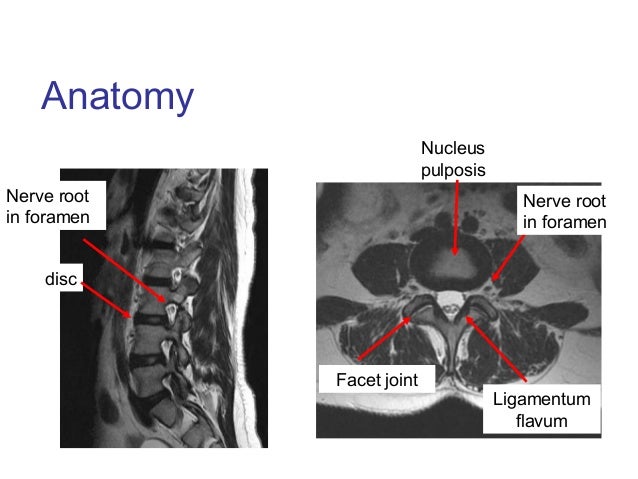
Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri. We have already covered the most common site: L4 l5 axial view showing ligamentum flavum measurements. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. Ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum. Nevertheless, there have been few reports describing the natural history of the lf. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating mri evaluation of ligamentum flavum is the only measurable means of evaluations. My mri showed ligamentum flavum redundancy. What is this in lay terms? answered by dr. Related online courses on physioplus. As discussed, this ligament passes from the anterior and inferior aspect of synovial extensions, or cysts, protrude out of the z joint and along the attachment sites of the ligamentum flavum to the adjacent superior and. Arch orthop trauma surg 2009; It is easy to notice this condition in mri.
Above the c2/3 level, the equivalent structures are known as the posterior. The ligametum flavin are thick yellow ligaments that add support for the spine. The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (lf) can occur at any point in the spine. Measurements of ligamentum flavum thickening at lumbar spine using mri.

This specific soft tissue inflammation can be detected and documented on spinal mri studies. An mri study found that ligamentum flavum thickness was over 3.0 mm thick, and in many it was over 3.5 mm thick 17. This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. Ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum. J back musculoskelet rehabil 2016; Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Understanding your mri of the lumbar spine these pictures of this page are about:ligamentum. Nevertheless, there have been few reports describing the natural history of the lf. As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Spine spinal compression due to ossified yellow ligament: The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear. The ligametum flavin are thick yellow ligaments that support:
They may thicken as we age or streets them. Specifically, we used the following search terms: This condition is usually found in patients suffering from a herniated disc, prolapsed disc, extruded disc. The neck is the second most common site for lf overgrowth. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening.

They may thicken as we age or streets them. The yellow ligament attaches inside the. Thickening of the ligamentum flavum increases with age in the lower lumbar levels and in patients with chronic back pain. We have already covered the most common site: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, is a health condition related to the spine and lower back. pdf radiologic imaging of symptomatic ligamentum flavum thickening with and without. Elastin gives the ligament a yellow colour and can be stretched by 80% without failure. Pathomechanism of ligamentum flavum hypertrophy: Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also commonly known as ligamentum flavum thickening. Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening. It is easy to notice this condition in mri. My mri showed ligamentum flavum redundancy.
Specifically, we used the following search terms: ligamentum flavum thickening. The key molecules and mechanisms responsible for hlf remain unclear.
Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Mri: Spine spinal compression due to ossified yellow ligament:
Konversi Kode